Generative AI & SEO- Important & Must Know Terms & Concepts
- Sep 14, 2025
- 5 min read
Generative AI is here and it is here to take your job - But only if you refuse to adapt and choose to ignore it. As a wise man once said, "AI is not here to replace human intelligence, it is here to replace human stupidity". And not updating yourself to keep up with the most important technology of our times is the height of stupidity.
As a digital marketer, it is even more important to keep yourself current. Since you are the expert, you have to know more about Gen AI than the general population so that you may educate your clients and customers about the best tools and technologies that is relevant to them. Learn about the tech behind the AI and the terms and concepts used in digital marketing and SEO and GEO today. So that your employers and clients feel reassured that they are working with an expert.
In this series of blogs, I'll briefly explore some of the crucial concepts in Gen AI. Lets start!
1) Vector Search

Vector search is an advanced search technique used in information retrieval, especially in machine
learning and natural language processing (NLP). Instead of searching based on keyword matches, vector search relies on transforming text, images, or other data types into vectors in a multi-dimensional space.
Each piece of data (e.g., a sentence, image, or document) is converted into a vector representation using embedding models like word2vec, BERT, or GPT. These embeddings capture semantic meaning.
When a search query is made, it's also converted into a vector, and the system searches for the vectors that are closest (i.e., most similar in meaning) to the query vector.
Vector search can significantly improve search relevance by focusing on the semantic meaning of the content instead of simple keyword matching.
For SEO, websites using vector search can deliver more personalized and contextually accurate results, boosting user engagement and satisfaction.
Related Concepts:
Embeddings: The process of converting text into a numerical format that can be interpreted by machine learning models.
Cosine Similarity: A method used to measure the similarity between two vectors in a multi-dimensional space.
2) Fan Out Queries

Fan-out queries refer to a process in search systems where a single query triggers multiple subqueries or searches across different datasets or systems, essentially expanding the query’s reach to fetch a broader range of results.
A single search query may result in several subqueries that go out to different databases, services, or even APIs. The results from these subqueries are then aggregated to provide a more comprehensive answer.
In SEO, fan-out queries can be used to aggregate information from various sources (e.g., product listings, blogs, reviews) to create a richer, more diverse set of results for users. This helps in improving search accuracy, especially for complex queries or when data is dispersed across different platforms.
Related Concepts:
Query Expansion: The technique of automatically adding related terms to the original query to broaden search results.
3) Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG)
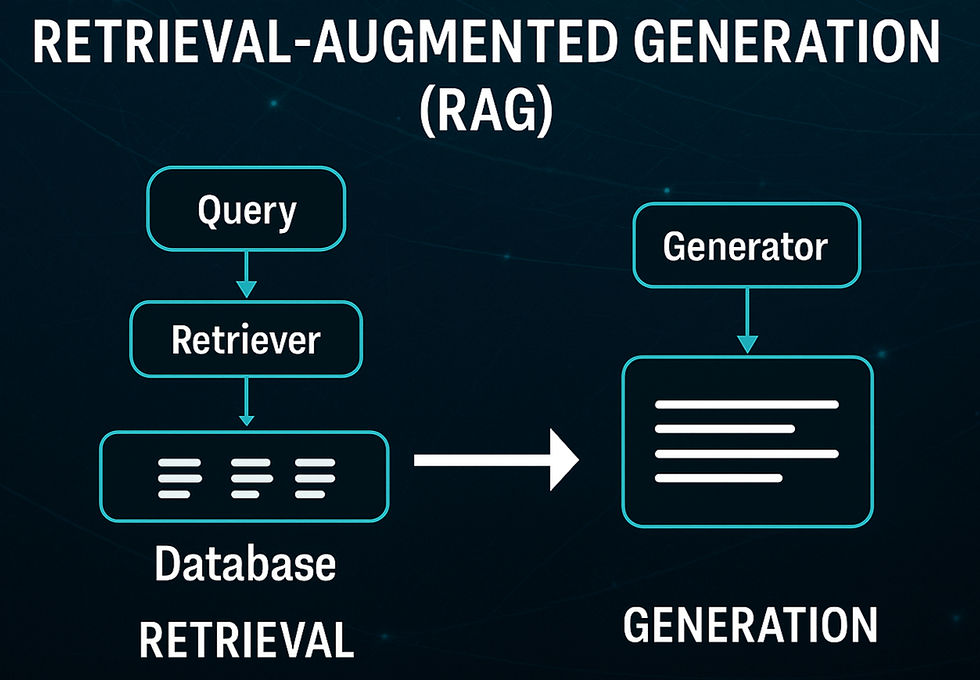
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) is an approach used in language models to combine retrieval (finding relevant information) and generation (creating new content) to enhance performance. RAG systems use external documents or databases to provide relevant context for generating answers.
RAG combines two components: a retriever and a generator. The retriever fetches relevant documents from a database or index, while the generator uses these documents to create detailed responses.
This technique is particularly useful in NLP tasks like question answering, summarization, or any task requiring both factual retrieval and text generation.
For SEO, RAG can improve the relevance and richness of search results by augmenting generated content (e.g., meta descriptions, blog posts) with contextually relevant data from external sources.
It helps deliver more accurate, context-aware results, enhancing the quality of content generated for web pages.
Related Concepts:
Neural Search: Search methods that combine machine learning and deep learning techniques for better retrieval.
Information Retrieval (IR): The process of finding relevant data from a large corpus of content.
4) Hallucination in Generative AI
Hallucination refers to a phenomenon in AI models, particularly in natural language generation, where the system generates information that is factually incorrect, irrelevant, or made up. It occurs when the model "imagines" details or presents false information confidently.
AI models, especially generative ones like GPT, may hallucinate when they don't have access to accurate data or when they're given ambiguous queries. They may fill in gaps with plausible-sounding information that isn't verified or factual.
Hallucination can harm search engine results, especially in AI-generated content, as it can mislead users or provide incorrect data. So a crucial part of SEO is ensuring a robust content validation process including fact-checking, accurate citations, and the use of trusted sources to prevent hallucination from degrading content integrity.
Using retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) can help mitigate hallucination by anchoring responses in accurate, externally retrieved documents.
Related Concepts:
Fact-Checking: The process of verifying the accuracy of information before it's published.
Content Integrity: Ensuring that the content generated and presented is truthful and reliable.
5) Prompt Sensitivity
Prompt sensitivity refers to how small changes in the input prompt (query) can lead to significantly different outputs from the AI model. Highly sensitive models may produce radically different answers based on slight variations in phrasing, structure, or wording.
LLM models may be highly sensitive to prompt structure, meaning that changing a word or rearranging a sentence can result in a different interpretation and output. This sensitivity is important to understand and be cognizant of when interacting with AI systems for SEO, as a subtle change in how a query is phrased can lead to different keyword rankings or content responses.
It's crucial to understand how to craft precise search queries and prompts that generate the most relevant results or content from AI tools.
It also highlights the importance of semantic search and query refinement, as small changes can lead to significantly different search results.
Related terms:
· Natural Language Understanding (NLU): The capability of AI models to understand and process human language in a way that’s semantically relevant.
· Query Refinement: The process of improving a search query to produce more accurate results.
A Quick Summary:
· Vector Search can improve relevance by understanding semantic meaning, driving more accurate search results.
· Fan-Out Queries expand the search's reach to multiple subqueries, improving the scope of results.
· Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) enhances generated content with real-time data retrieval, boosting content accuracy.
· Hallucination presents a challenge, particularly for AI-generated content, requiring strong validation of facts.
· Prompt Sensitivity emphasizes the importance of precise query crafting in AI-driven search systems.
These terms represent key concepts that help us understand search optimization in the new world of AI , especially as semantic search and machine learning continue to shape how search engines rank and present results. Understanding these concepts will help you to explain AI integrated SEO strategies to your team and clients and better optimize for both human users and AI-powered search systems.



Comments